![]() Electronic components
Electronic components
|
|
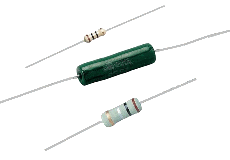
Resistor : unit = Ohm A
resistor serves to determine what current intensity circulates in a place of
the electronic circuit . It can
serve, according to the formula U =R x I , to
determine what tension there will be to its extremities . Values vary from almost zero
ohm to several millions of ohms (
mega ) . The
using limit is the power (
in watts ) that the
resistor can support . |
|
|
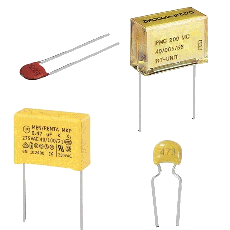
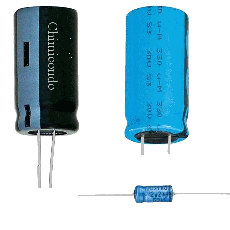
A capacitor
allows passage of the alternative current but not the direct current . It can serve to decrease
or increase some frequencies of alternatives signals (
filters ) . Electolytic capacitors ( to
the right ) have a connection’s direction .
The negative extremity is indicated . They have also a
great capacity ,
that allows them to store a quantity of electricity .
Values vary from
some picofarads to several thousands of microfarads . The
using limit is the voltage ( in volts ) that the capacitor
can support . |
|
|
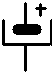
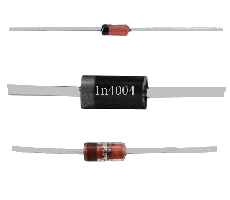
Diode : A diode alows passage of electric current only in a direction . It serves mainly to straighten an
alternative current to transform it into direct current . The current
circulates between the extremity without ring to that witch as one ( according to the arrow of the symbol ) . If four diodes are associate in an alone cast block , we call it a bridge (
connectors ~ ~ + and - ) . The
using limit is the intensity ( in amperes ) that the diode
can support . |
|
|
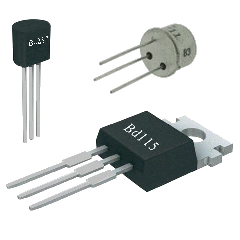
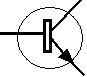
Transistor : A transistor serves
mainly to amplify electric signals . It can equally serve as switch for example to control
a relay . There are two
types of transistor : NPN and PNP according to the direction
passage of the current . There are three connectors :
the base control the current that circulates between the collector and
the emitter ( E : arrow on the
symbol ) . Transistors have
different gain and power according to the model and often the size . There are
components that have the format of a transistor but can be: regulator, triac, double diode . The
using limits are the intensity ( in amperes ) or the power ( in watts ) that the transistor can support .
|