![]() Theory of electricity
Theory of electricity
Molecule: The molecule is the smallest possible part of
a physical element , Example : a molecule of water (
H2O ) is always water .
Atom: The atom is an element of the molecule ( it is no longer a physical element ) . Example : two atoms
of hydrogen and one of oxygen give a molecule of water .
The atom is
constituted by a nucleus around of which turn electrons . In elements like copper wires the electrons
can leave atoms .
Electricity: If
we connect something between the poles of a current’s generator we create an electric
circuit , electrons form
a current that circulates from a pole to the other .
|
|
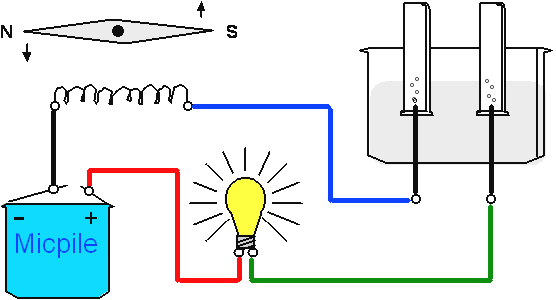
The electric
current that circulates from the battery has three effects : it lights
the bulb , it provokes the electrolysis of the
water and it deviate the needle of the compass . The electric
current has a thermal effect , a chemical effect and a magnetic effect ( a magnetic field
can create the movement of an engine ) . We can compare
an electric current to a liquid that circulates in pipes , An example is a central heating
. The
battery would correspond
to the boiler and the bulb to a radiator . |
We can generate an
electric current by the chemistry ( battery,
accumulator ) or by the magnetism ( dynamo, alternator ) .
The magnetic
effect is reversible : a loud speaker produces a sound but it can
also serve as microphone ( in an intercom ) .
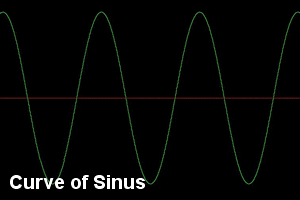
The current can be
direct ,
it circulates then in one way ( battery , accumulator ) , or it is
alternative : it circulates once in
a way
then in the other ( line, sounding signal ) .
The voltage of the
line ( in
We consider since
the discovery of electricity that the current circulates between the pole + to
the pole - . In reality this is the
contrary because electrons are negative ( - ) .
Anecdote : If we drive in a potato a stem of copper and a stem of zinc we obtain a battery : the potato’s battery ( not very powerful ) .